HealthTech has been undergoing significant transformation since the world began dealing with Covid-19 in 2020. Healthcare providers are investing heavily in new technologies and medical digital solutions. DigitalMara has studied the latest trends and compiled a list of directions in which healthcare technologies are evolving. The pandemic greatly boosted technologies in the medical field, such as enhanced workflow and delivery of treatments and services, process automation, medical education improvement, smart devices, and much more.
Big companies are putting serious capital into technologies for healthcare and projects in collaboration with universities and other institutions. For example, Microsoft projects are working on infection prevention and control, treatment and diagnostics, mental health, and return to work after illness. The Google Health subdivision is working on developing tools and initiatives in the field of AI.
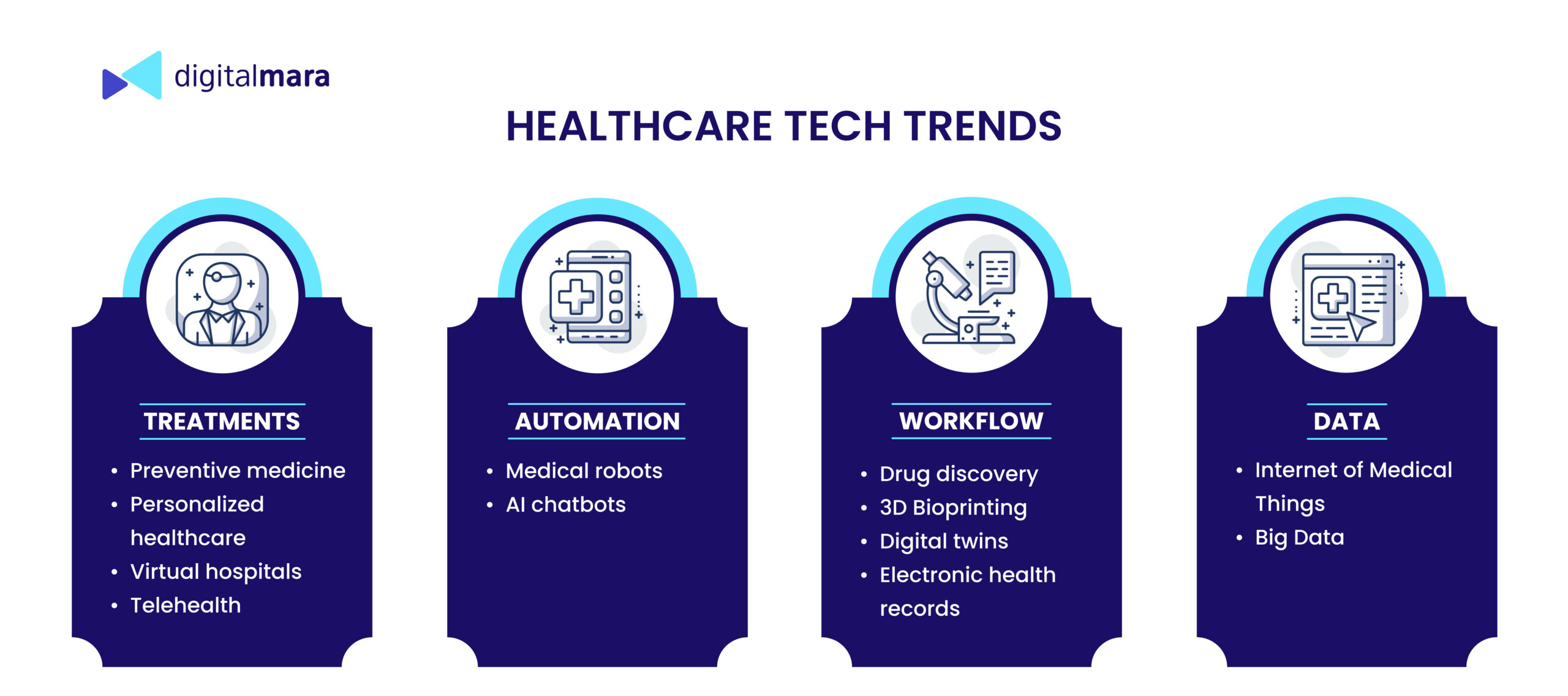
Trend 1 – Remote healthcare
During the pandemic, remote healthcare gained popularity, and it continues to evolve. This can provide timely and easy access to certain kinds of care at a reduced cost. Remote care is often appropriate for people with chronic diseases who need constant monitoring. Doctors can monitor symptoms, change medication intake and keep an eye on patient behavior.
- Virtual hospitals
A virtual hospital is one without a physical location, designed to provide continuous distant patient care using IoT, telehealth, AI, and cloud technologies. Patients get access through a web portal or a mobile application. Virtual hospitals can deal with chronic illnesses, allergy treatment and mental health, allowing staff to watch over many more patients simultaneously.
- Telehealth or telemedicine
Telehealth services have been employed for some time now. But the pandemic led to rapid growth of these systems, which can be based on various communication technologies, including video conferences, apps, and streaming services, to provide healthcare services remotely. Patients can get medical assistance and care from their homes or anywhere and send messages to the provider. This is an advantage for elderly people, people with disabilities, and people who live in very remote locations. Doctors can provide consultations and even monitor vital signs remotely. Telehealth systems make it possible to store and access a patient’s medical history and to transfer data from wearable devices.
Trend 2 – Wearable devices
There are two types of wearable devices predicted to become more popular rapidly. The first is devices designed for individuals to track their own health indicators and fitness activities. The second is clinical medical devices that allow for monitoring patients remotely. Such tools are already being used successfully to detect and monitor physical illnesses. But developers also see the potential of the technology to help define symptoms of mental illness.
- Internet of Medical Things
IoT in healthcare is sometimes termed IoMT — the Internet of Medical Things. Such devices have come a long way from simple trackers of heart rate and blood oxygen levels to much more complex devices, such as smartwatches that can produce ECGs, smart tissues for detecting blood pressure and predicting the risk of heart attacks, and smart gloves to reduce the trembling of patients with Parkinson’s disease.
The idea is to design wearable devices that are autonomous, meaning they will include an internal processor so data doesn’t need to be transferred between the cloud and the device for processing, and analytics are performed internally. This solves data privacy issues, as sensitive data stays inside the device. The second advantage is improved speed, which is especially important for detecting a health threat and warning the user in real time.
Trend 3 – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The market size of AI and ML tools in healthcare is expected to reach $20 billion in 2023. The technology is capable of analyzing large datasets more accurately to detect diseases, to help in development of medications, and to improve diagnostics procedures. Using AI can significantly reduce the number of false positive results.
- AI chatbots
Chatbots can be a part of medical consulting. These tools are available 24/7 and can be used on clinic and hospital websites and in mobile applications, which may be helpful in situations when prompt medical assistance is unavailable for some reason. They are able to conduct preliminary medical diagnostics and provide information on health issues based on patient feedback and complaints. Chatbots can help to define next steps and lead the patient to a doctor.
- Drug discovery
AI and ML can help in certain phases of medical drug research, for example creating model molecules and simulating chemical reactions in multi-factor environments. This can decrease spending on reagents and laboratory equipment and increase the speed of development.
- Preventive medicine
Preventive medicine means predicting illness and treating a small problem before it becomes a big one. It may involve, for example, dealing quickly with outbreaks of infectious diseases or decreasing the chance of rehospitalization or evaluating the impact of lifestyle factors on the population’s health. Artificial intelligence can identify patterns in huge datasets and allows for making more accurate predictions.
- Personalized healthcare
AI creates the opportunity to receive personalized medical care, which encompasses the concept of precision medicine — prescribing drugs and other treatments tailored to the patient’s age, genetics and risk factors. Such information can help to predict a drug’s efficacy and side effects. Personalized healthcare also involves giving patients greater choice about how their medical care is planned and delivered. Personal treatment plans are based on individual circumstances, opinions and beliefs.
Trend 4 – Clinical automation
The main idea here is not to replace people with machines, but to help clinical staff in their everyday activities. For example, patient transportation, remote diagnostics, assistance in surgery, hygiene and sterilization, drug delivery and more.
Trend 5 – Cloud technologies
Large amounts of structured and distributed medical data, for example patient records and DICOM files, are generated every day, which need to be stored, combined and managed efficiently. Secure cloud-based solutions, such as electronic health records (EHR) and practice management software, can help here. Cloud solutions are scalable and available at any place and any time. They are convenient for either health providers or patients.
EHR systems are gaining wide popularity for their security and transparency. They accumulate and analyze data, visualize it with charts, graphs, and diagrams, and most important, improve work with patients. The last type may provide patients access to lab test results, let them order a repeat prescription, fill in forms, send a message to their doctor, and check their appointments, while doctors can fill in patient cards, monitor dynamics, and write prescriptions.
Trend 6 – 3D Bioprinting Technology
3D printing technology has big potential in healthcare, for example in developing personalized prostheses, assistive devices, and implants for various purposes. Bioprinters are able to create organ-like structures using live cells, molecules, growth factor proteins, and biological materials. In general, bioprinting allows for decreased costs and production time, making implants and prostheses more affordable and more easily customized.
This technology has not yet become basic in clinical practice. Scientists believe that, eventually, they will be able to print bones and even entire organs.
Trend 7 – AR/VR and Digital twins technology
Augmented or virtual reality technologies have potential in both diagnostics and education. Medical students may use virtual 3D models of organs for learning theory and simulating surgeries and real cases for practicing their skills. With AR, one can also add additional information to real objects and access that information using voice commands and a hands-free mode. VR reality can be used as part of therapies for chronic pain and anxiety.
- Digital twins
Digital simulations of organs and systems can be used for a variety of purposes: for testing drugs and experimenting with treatments, or for research into diseases and pathologies. The virtual models being created are geometrically and physically accurate and are tested in a virtual environment. This can help shorten the time before release of a medication, while reducing the risks and costs of testing on humans and animals. In the future, we may have models of the whole human body.
Trend 8 – Big Data and analytics
Huge amounts of healthcare data have been accumulated over the years. Based on this data, scientists can discover medical patterns and determine correlations between people’s health and factors such as demographics, ecology, economy and others. Healthcare data analytics can be used to improve medical care and clinical operations, measure the effectiveness of treatment and to prevent diseases.
Using these technologies, health providers can obtain and analyze information about performance in real time so as to make better decisions. Using analytics, they are able to allocate and manage resources more efficiently, prepare employee schedules, control medical supply inventory, and reduce medical errors.
Legacy healthcare software challenge
A lot of healthcare organizations are still using legacy software systems, vulnerable to risks such as potential data leaks, system failures, cyberattacks and incompatibility with modern software platforms and services. An important factor in the move to a more modern platform is the need to verify compliance with current standards such as HIPAA requirements. Modernization of the old system can be carried out in various ways: migration to a modern healthcare platform or operating system, or rebuilding and restructuring components or the entire system.
Final words
Digital transformation of healthcare demands a lot of resources and deep technical knowledge. Both proactive startups and big companies are bringing IT innovations to the market that are introducing new technological trends in healthcare. In turn, healthcare providers are cooperating with software developers extensively, helping to create a toolset for significant innovations in the future of healthcare.