The financial industry is facing many challenges, such as global economic uncertainty, the lingering impact of the pandemic, data security threats, changing regulations, outdated software, and new demands and preferences among customers. FinTech companies, financial service providers and conventional banks compete to provide the best product and experience for customers. They implement new models such as open banking, BaaS and neobanks, and various types of digital payments. DigitalMara has reviewed some of the main trends in FinTech and their application.
Lots of banks are still using legacy systems in everyday operations, whilst receiving and processing large amounts of sensitive data. This outdated software can result in extensive outages and vulnerabilities, which is especially critical with the increase in cyberthreats and financial crimes. It also hinders digital transformation and often results in a negative experience for customers. Cloud computing, advanced APIs, RPA-automation, AI and ML are parts of a modern toolset for modernization of legacy systems in banking.
The means of accessing and managing bank accounts, paying for goods and services, and taking out loans are changing, for the most part going digital. Meanwhile, usage of digital wallets has increased significantly, in keeping with the number of digital transactions worldwide. According to Statista, the sum of such transactions reached $8.38 trillion in 2022 and is expected to reach $9.47 trillion in 2023. Customers expect from vendors various types of digital payments like p2p, embedded, BNPL, contactless and others.
Financial service providers must cope with a large number of transactions and at the same time ensure data security and privacy. Finance is one of the most heavily regulated industries, with strict compliance requirements. Expanding cybersecurity threats underscore the need for fintech regulation and expanded RegTech capabilities. The spread of digital banking has also led to issues surrounding data ownership. For example, Blockchain promises to implement a decentralized network model and to make peer-to-peer transactions instant and free.
Artificial Intelligence is still a crucial part of innovation in the finance sector. It brings greater accuracy to processes, provides for data-driven decision making, and enhances overall efficiency. The technology not only works with large volumes of data and customer service, but also helps prevent cybercrime and financial fraud.
And don’t forget about FinTech APIs that bridge the gaps between banks, third-party distributors, websites, mobile apps, and customers, and enable secure data exchange between them. This tool simplifies adding new features and integrations, as well as creating new product lines, and allows users to create an omnichannel experience. Also, Open APIs can be part of regulatory compliance, ensuring efficient transfer of customer data to the outside world while maintaining data security.
Trend 1 – Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
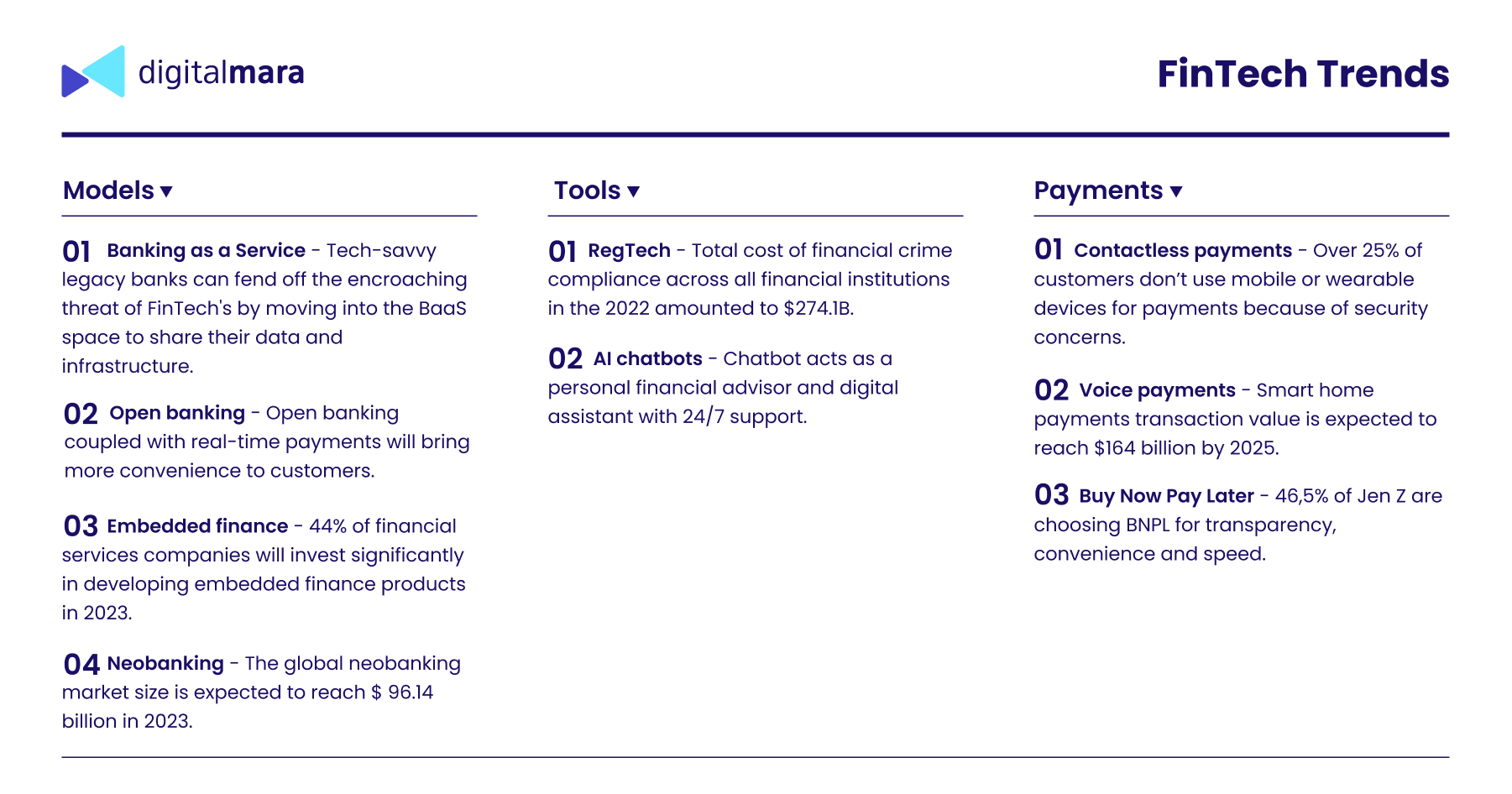
The Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) model solves the problem of licensing for non-banking businesses that want to have digital banking services inside their app or website, like payment services, loans, mobile bank accounts and debit cards. All regulatory issues, compliance and data security are the responsibility of BaaS providers. In partnership with banks, companies can launch co-branded or white-labeled credit cards and other products.
BaaS empowers almost any business to be a banking provider with some coding. Using APIs, the company can integrate banking services into its products and bring additional value to its customers. BaaS providers are responsible for risk management and fraud protection, KYC and PCI compliance, cards and money flow management.
Trend 2 – Embedded finance
According to Mckinsey, embedded finance is a new form of partnership between banks, technology providers, and distributors of financial products via non-financial platforms. For example, e-commerce, insurance, accounting platforms, airlines and others. Such platforms simultaneously fulfill product and financial needs, and provide a convenient, easy-to-use customer experience.
In general, embedded finance products are represented as deposit, payment, issuing card, and lending. Distributors include retailers, business-software firms, online marketplaces, platforms, telecom companies, and original equipment manufacturers. They can create additional value for customers and increase their revenue, without taking on bank operating costs.
Trend 3 – Payments
Payment methods are also changing according to the needs of customers, delivering more flexibility, ease and convenience and going more digital. And in-app purchases and peer-to-peer (P2P) payments keep growing.
- Contactless payments
Contactless means making electronic transactions from mobile devices via app or wallet and wearable device. Using contactless payments, one can pay bills, make purchases and send money, with all data stored directly in the mobile device and protected from unauthorized access. Each transaction generates a one-time specific code for a specific transaction as protection against fraud. Payments are based on short-range wireless technology and the availability of NFC (near-field communication), MST (magnetic secure transmission) and POS terminals with support for contactless operations.
- Voice payments
Voice technologies are changing how customers do things. Statista predicts the number of voice assistants to reach 8.4 billion worldwide. Voice payments can be used in many ways: to send money to a person, pay a bill or pay for services, buy groceries, tickets or other goods, make reorders, and also check account balances and monitor payment schedules. Customers just need to link their card or bank account to a mobile phone.
Traditional banks like Wells Fargo, on the other hand, are adding conversational voice interfaces to their mobile banking apps to allow their customers access to all banking services. AI algorithms are used to distinguish the voice congruence of the card holder through a voice biometric system and block any unauthorized payment. The system has to recognize various accents to avoid misunderstandings. At real points of sale, the ability to accept voice payments involves being equipped with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth-enabled systems, sensors, and in-store cameras.
- BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later)
BNPL is an alternative form of lending or credit card that has spread in e-commerce. For the moment, this payment method is also being used for everyday purchases like grocery and fuel, and for paying bills. Customers are able to buy on a BNPL basis in stores or online with zero interest, making it flexible. The payment is made weekly, fortnightly, or monthly, and interest is only charged when the payment is late. The seller pays the commission to the lender. The cost of offering BNPL may be offset by increased sales volume and also gaining customer trust and loyalty.
Core features of a well-designed BNPL solution are the ability to split payments, loan terms, convenience, repayment frequency, purchasing power and customer support. Also, the solution should be robust and scalable, to handle a high volume of transactions. One of the serious sticking points here is credit checks on customers, who may have debts across multiple platforms. Another is the mechanism of collecting money, which can be solved, for example, through direct debit or gamification.
Trend 4 – Open banking
In the open banking model, non-bank businesses get access to data from their customer’s bank account to provide account insights or initiate payments from an app or website. It is a way to enhance financial literacy, trust, and engagement with consumers. The model becomes the basis for financial service and financial management apps and platforms. The benefits are better and faster access to account data and ability to conduct account-to-account (A2A) payments. Customers can better control their finances, improve financial habits and make decisions in a better way.
Experts name open banking as a “pay with bank” option, as it cuts fees from card use while paying. This is an advantage for such payments as recurring phone bills, utilities, and others and also instant payouts and subscription payments.
Open banking providers connect to the bank’s system via the API to receive transactional data; meanwhile, banks have to ensure reliable and consumer-permissioned access to data. This data can also be used in AI and ML–based risk models to build more reliable authentication strategies and protect consumers against fraud.
Trend 5 – Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
Regulatory Technology is constantly evolving as FinTech advances, more financial services appear and businesses apply new digital models. In the absence of proper regulation, the financial environment is more easily and more often exposed to fraud, hacking, data leaks and other security threats. RegTech creates a streamlined compliance process, makes regulations transparent, and handles all digital assets.
RegTech should be used in the early startup stage as a part of an assessment of product–market fit strategy, for licensing and to fulfill all regulatory requirements. Also, this model the adaption of environmental, social, and governance principles in financial activities. Much attention must be paid to regulating cryptocurrencies, since they are subject to risks and manipulation, such as tokens with unregistered securities.
RegTech covers a number of procedures, such as risk management, regulatory reporting, identity management, compliance and transaction monitoring. Technologies such as Big Data, cloud computing, and Machine Learning algorithms allow for automating and improving KYC (know your customer) and reporting processes, provide greater accuracy and speed, uncover hidden risks and threats, get compliance insights, predict market changes, and perform anti-money laundering analysis.
Trend 6 – AI chatbots
Chatbots simultaneously answer two needs, for contactless service and online communication. Powered with AI and natural language processing, they are evolving into intelligent digital assistants. Bots help to improve both the quality of digital service for customers and the employee experience. They are trained using knowledge about the customers’ financial history and their behavior patterns, and based on this provide improved, personalized experience, while streamlining certain processes. Bots can assist in a wide range of operations: opening and managing accounts, providing balance details and other information, making payments and transfers, giving recommendations, sending reminders and others.
As they work with financial operations and sensitive information, banking chatbots should be reliable and precise and follow data privacy and security standards. Only authorized personnel should get access to received data. Also, bots should be available on various platforms in order to provide a consistent user experience across multiple devices.
Trend 7 – Neobanking
A neobank is a fintech company that offers traditional bank services such as payments, money transfers, and lending via the web or mobile platforms. They are not regulated the same way as conventional banks are and don’t have physical locations. To strengthen their position, they often cooperate with regulated, licensed and FDIC-insured entities and integrate with trustworthy PCI DSS-compliant payment platforms. Neobanks have few products in order to mitigate risk and reduce costs, however they can offer lower or no-fee products and more competitive rates.
All operations are digital, with a promise of a seamless and fast online user experience. Customers can open an account on their own in a few minutes. Usually, apps provide a simple, user-friendly interface and intuitive workflow. Among some primary features are expenses, payments, transactions history, notifications and customer support. Obviously, the neobank must ensure an adequate level of security. They use two-factor or multi-factor authentication, dynamic CVV2, data encryption and the ability to lock or freeze the account any time through the app.
Final words
This year will be a significant one for FinTech. Vast technological transformation, new regulations and customer expectations have a great impact on the financial industry. Financial institutions that want to succeed would do well to implement modern approaches and follow trends in financial technologies.
The DigitalMara team can be your reliable partner building FinTech solutions, from payment automation, integration of payment systems and invoicing, to modernization of legacy systems and building a customized, full-fledged finance product.