Chatbots have become increasingly popular in recent years, both for business and internal purposes. Statista estimates the market will reach about $1.25 billion by 2025, with growth driven by the emergence of cost-effective open-language models like ChatGPT. Automation, omnichannel experience, the ability to handle a large volume of requests simultaneously, personalized communication, and cost savings can be gained with chatbots. Read on as DigitalMara shares some insights and recommendations for chatbot development.
Google trends show exponential growth of interest in chatbots since November 2022. Recently, the search has been closely related to Artificial Intelligence, OpenAI and GPT-3.
Chatbots have started as pre-written scripts based on keywords and pattern matching to respond to users’ queries. They can conduct structured conversations and answer most common questions about products and services, as well as handling some repetitive tasks such as asking for feedback, logging a request, and redirecting the conversation to custom support. These chatbots are easy enough to set up.
Now, technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing are empowering chatbots to carry on more human-like communications. Chatbots can understand human language, analyze queries, understand behavior patterns and in response provide more accurate information and personalized recommendations. Also, they are able to interact with users via text and voice. Companies and businesses are adapting AI-chatbots for their advanced capabilities, although these do require more sophisticated development.
Chatbots use cases and industries
Chatbots are often the first contact point for a business and create the first impression for customers, offering round-the-clock support and quick answers to questions. Businesses and organizations across various industries can optimize their processes, saving time and making things simpler.
In general, as part of customer service, chatbots do the following:
- provide responses to users’ queries,
- provide detailed information about products and services,
- give personalized recommendations,
- assist in resolving complaints and other problems,
- allow users to take various actions, such as making orders, payments, appointments, or reservations, completing registration, etc., and
- collect user feedback about products and services.
While each domain has its own specifics, depending on the embedded program, chatbots can solve tasks from the simplest to super-sophisticated.
E-commerce & Retail
The most saturated industry is e-commerce, where chatbots are pushing the boundaries of the shopping experience. Customers can get assistance finding items, getting information about product availability, detailed descriptions and reviews, and also personalized recommendations based on their preferences and browsing history. Additionally, via chatbot they can pay for the item, order delivery, track their order, cancel the order, get a refund and change personal details.
In retail, the role of chatbots is pretty much the same. Customers, for example, can get real-time inventory updates in a particular location and alternative options if the desired item is out of stock.
Healthcare
Chatbots in healthcare may improve service and make it more accessible for patients. They can help with basic inquiries, such as finding a nearby healthcare facility or scheduling appointments; provide general health information, answer questions about symptoms or medications, and offer self-care advice for minor ailments. Chatbots in health apps can monitor patients’ vital signs, remind them to take medication, track their physical activity and nutrition, and signal when there is a need to see a doctor. Mental therapy, health and wellness apps also have chatbots that provide support to users, analyze their lifestyle and determine their current status.
Banking and finance
In the banking and finance industry, chatbots help customers manage their finances more efficiently and make more informed financial decisions, including personalized financial advice. Chatbots can assist with basic banking transactions, such as checking account balances, transferring funds between accounts, and making payments. They can also help with more complicated tasks such as creating budgets, tracking expenses, and setting savings goals.
Insurance
The most important task for chatbots in the Insurance industry is to assist with claims processing: they can help customers understand their coverage, file claims, and track the status of their claims. Chatbots give customers the opportunity to better understand policy terms and conditions, choose the right insurance policy for their situation and make informed decisions about their insurance coverage.
HoReCa & Travel
In the HoReCa and travel industries, chatbots can assist in making a reservation of a table or room, booking a flight or apartment, checking booking status, and paying the bill. Customers are able to make an order from the menu, on-site or for delivery, check detailed information about menu items and ingredients, and change and supplement their orders.
All in all, chatbots can serve pretty much all industries. We can add telecommunications, gaming, education, automotive, entertainment and even government to the list. Today, many companies also implement internal chatbots to support the employee experience and reduce costs. Chatbots may assist with IT issues, HR procedures, training, benefits and deductions, conference room reservations, notifications, vacation and time-off policies, and others.
Chatbots and customer experience
Customers who have a positive experience are more likely to show brand loyalty and contact the chatbot again. However, not all customers are happy about chatbots. In fact, many say chatbots are really annoying. According to a Forrester study, 50% of customers feel frustrated using them, and 40% of their interactions were negative. That leads to a negative brand perception and avoidance of chatbots in the future.
Users’ complaints about chatbots include:
- Human interactions are better and more personalized, as chatbots lack empathy and understanding.
- Chatbots are too rigid and unable to understand and handle complex queries or nuances.
- Chatbots are limited and provide inaccurate responses or responses that don’t make sense in the context of the query.
- Past negative experience with chatbots, such as receiving irrelevant responses and technical issues.
- Privacy and data security when interacting with chatbots.
- Customers with disabilities or language barriers may find it difficult to communicate efficiently with chatbots.
Developers are working to solve these problems, expand the capabilities of chatbots and improve the service so that customers will see a benefit in having virtual assistants to deal with a wide range of situations, with the opportunity to get the desired result faster and more smoothly. Artificial intelligence technologies can make chatbots smarter and increase their potential. Here are some benefits:
- Omnichannel experience – Chatbots can be part of a seamless omnichannel experience, integrated with various channels such as social media, messaging apps, and websites. This allows users to get consistent and personalized interactions across all touchpoints. They can even start a conversation with a chatbot in one channel and continue in another.
- Inclusive experience – Chatbots can be useful for people with various disabilities. Text-based conversations for people with hearing impairments, voice recognition for visual impairments or dyslexia. A chatbot can also help people with cognitive impairments such as autism or ADHD by providing clear and concise information in a structured format. They can also repeat the information as many times as necessary, which can be useful for those who have problems with memory retention.
- Multilingual opportunities – A single chatbot can be trained to understand and respond in different languages, without the need to create a separate chatbot for each case. This is helpful for companies who are going global and expanding the audience.
How to develop a chatbot
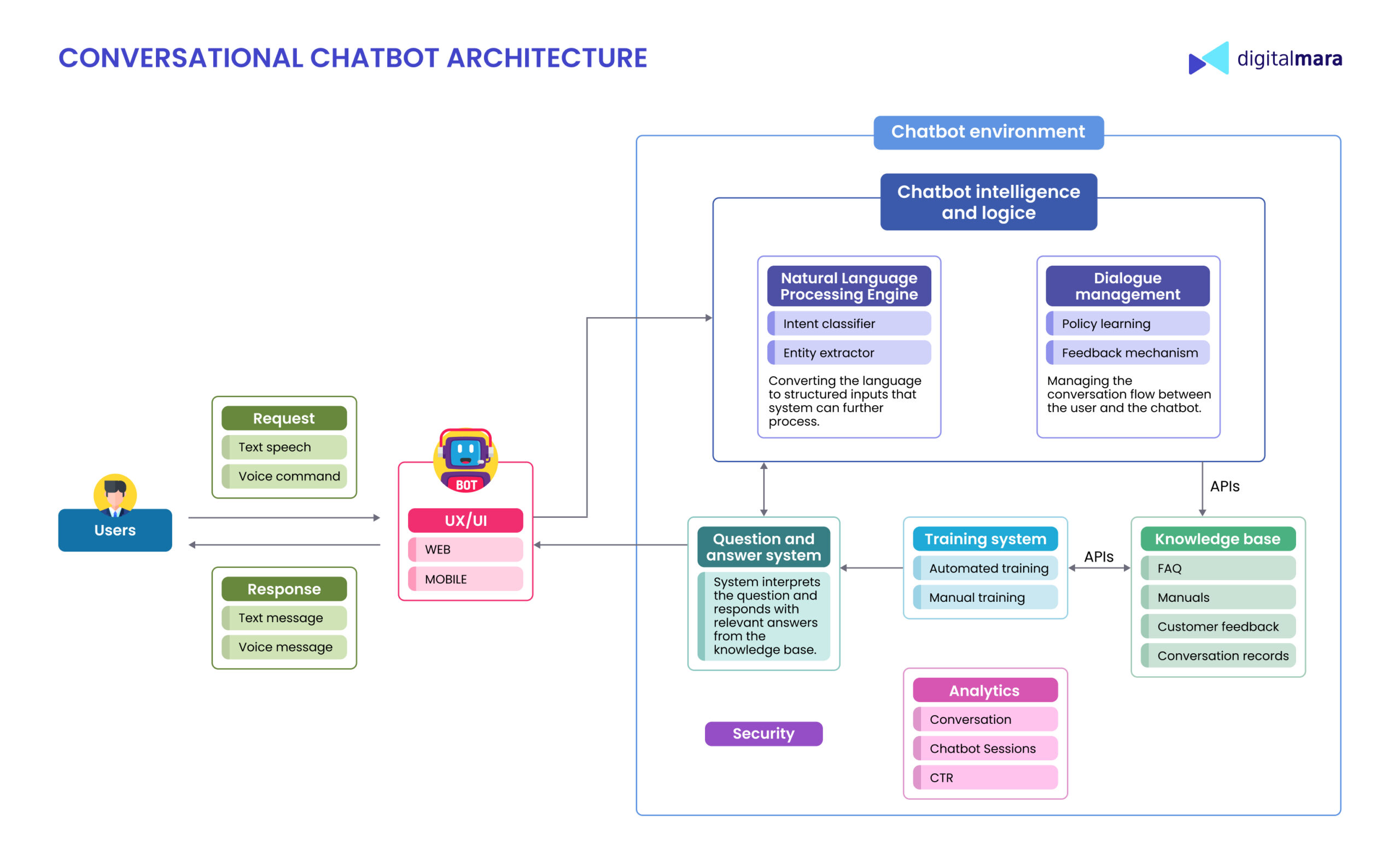
Development of any chatbot starts with defining its main goals and functionalities and understanding what tasks it should perform and how it will interact with your users. The basis of any chatbot is data. The more precise the data, the more efficiently the chatbot will work. Chatbots can get information from generated databases, user inputs, social media and other open sources. Therefore, data collection is also a crucial part of the development process.
Today there are especially popular out-of-the-box solutions — no-code and low-code chatbot builders, which can be an effective solution to save budget and time. These tools provide drag-and-drop building blocks, access to word cloud generators and integration with your software via APIs. However, these solutions won’t allow you to build a customized chatbot with a wide range of tasks based on the specific needs of the users or the company or organization.
The DigitalMara team has vast experience in developing chatbots for the web, mobile apps and messaging platforms. We use a modern tech stack, including Python, with frameworks like Flask or Django, Node.js with Express.js and Java with frameworks like Spring Boot. However, if the project requires, we also can work with no-code and low-code builders. If you want to make your chatbot intelligent, we know how to do it with AI technologies. Such conversational chatbots process users’ inputs and make replies more personal and accurate.
After it has been determined what your chatbot will do, what problems it will solve and which users it will serve, the following steps are:
- Creating conversational architecture, which means we build the flow and structure of the conversations the chatbot will have with users.
- Collecting data to train the chatbot. The client may have a ready-made database; we can help supplement it or collect data from scratch.
- Integrations with various systems like internal software (CRM, ECM, ERP), messaging platforms (Facebook, Slack) and third-party services. It is implemented via the API.
Analytics dashboard to collect valuable insights about users, including the usage level of the chatbot, popular queries, and how well the chatbot performs. With these metrics, one can improve business processes and operations and make informed business decisions.
Like any software product handling data, chatbots should comply with data privacy laws and regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, as in California, and other local laws and regulations. In addition, they need to comply with industry-specific regulations where they will be used. For example, for the healthcare, insurance or banking sectors.
Summary
Chatbots can’t completely replace customer service. They have the potential to improve people’s lives through round-the-clock access to information and basic actions, which can be especially useful for the financial and healthcare industries. Commercial brands can use them to enhance the customer experience and gain more loyalty.